4C Diamond
Brahma Diamond’s Guide to buying diamonds
4 C’s of diamond quality is the universal method for assessing the quality of diamond anywhere in the world. It is the globally accepted standard for describing diamonds- Color, Clarity, Cut & Carat weight. These parameters help to select the best & right quality diamonds.
Cut
The cut of a Diamond refers to how well a diamond is cut and polished. The perfect cut is properly proportioned, aligned and beautifully polished so that the highest amount of light can reflect out of the stone. A well-cut diamond will shine brightly, while a poorly cut diamond will appear dull and lack-luster. A good cut gives the diamond its brilliance, fire and scintillation. When diamond is properly cut and shaped, its ability to reflect and refract light increases greatly.
It refers to how the facet of a diamond interacts with light. It is determined by factors such as symmetry, proportion & polish. Brahma Diamonds, from the smallest to largest stone are cut to exacting standards. The cut affects how a diamond reflects the light.
Each diamond is assessed and graded on its cut quality, known as the diamond cut grade. The Cut Grade of a diamond is assessed on different factors such as brilliance, fire, symmetry, and polish and ranges from excellent to poor. The higher the cut quality of a diamond, the more sparkle it is likely to have. Diamond cut grade directly impacts its beauty.
Excellent: An excellent cut diamond is perfectly proportional and has the best symmetry, brilliance, fire and polish. An excellent or ideal cut diamond reflects almost all of the entering light, so the diamond sparkles beautifully.
Very good: A very good cut diamond offer exceptional brilliance and fire. It reflects a large majority of the entering light. A very good cut diamond provides similar sparkle to those of excellent grade.
Good: A good cut diamond showcases brilliance and sparkle, by reflecting a substantial amount of light entering it. A diamond with a good cut is a more affordable choice.
Poor: A poor cut diamond is a diamond that has been cut too deep or too shallow. A poor cut diamond has significantly lower in price than any other diamond cut grade while also lacking sparkle.


Carat
Diamond carat refers to the overall weight of a diamonds. 1 carat is the equivalent of 0.200 grams or 1/5 gram. Diamonds range in weight from a fraction of a carat to several carats. Even a fraction of a carat can bring a considerable difference in the price of a diamond. Hence, the point system is used to maintain precision in weight, thereby determine its monetary value. Carats are divided into points where 1 carat equals 100 points. For example,
- ½ carat diamond or 0.50 carat diamond – 50 point
- ¼ carat diamond or 0.25 carat diamond – 25 point
A common misinterpretation about carat weight is that bigger is always better. In actuality, a higher carat diamond with a poor cut can appear smaller than a lower carat diamond with a high quality cut.
Diamonds which look visually bigger weigh less in reality because of the way they were cut make them a lot less valuable than a diamond cut in a standard way which looks smaller but there is more mass in the actual stone. Choose diamonds that are cut very well. They tend to have less depth and more spread.
Diamonds are available in a variety of shapes and weights. One-carat diamond costs more than twice that of a ½-carat diamond (assuming Color, Clarity and Cut grade are the same). Two diamonds containing the same weight may be unequal in value due to the difference in cut, clarity and color.
There is a difference between ‘Carat’ and ‘Karat’ and shouldn't be confused at all. ‘Carat’ denotes the weight of a diamond and ‘Karat’ denotes the weight of gold.
Clarity
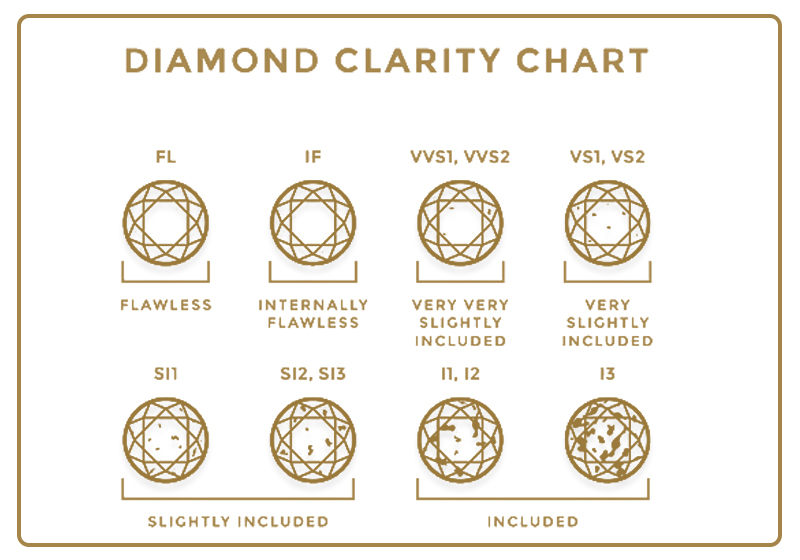
Diamond Clarity refers to the measure of the purity and rarity of the stone, graded by the visibility of these characteristics under 10-power magnification. It is graded as flawless if there are no visible internal flaws & external imperfections under 10-power magnification. The clarity of a diamond is the assessment of small imperfections on the surface and within the stone. While imperfections are often invisible to the naked eye, clarity is still important to the overall brilliance of a diamond.
Diamond Clarity is an important characteristic that determines a diamond’s beauty. From all of the 4Cs, diamond clarity is an important consideration when buying a diamond. The clarity of a diamond is inversely proportional to flaws. The lesser the flaws, the higher the clarity grade of a diamond will be. The clarity of a diamond can also affect on its value. A diamond with high clarity is a lot costlier than a low one even if they have the same cut, color and carat value.
There are 5 diamond clarity factors:
Size: The more or larger noticeable a characteristic, the lower the likely clarity grade.
Number: The more characteristics, the lower the clarity grade. Fewer characteristics tends to a higher clarity grade.
Position: This position turns inclusions into reflectors, which have a bigger impact on the clarity grade.
Nature: The nature of a diamond characteristic relates to its impact on durability and the type of inclusion.
Color or relief: Color or relief is essentially a measure of how much contrast there is between the characteristic and surrounding diamond or how easily a characteristic is seen.

Color
It refers to the tint inherent naturally in diamonds, most of the white diamonds have a slight tint of yellow. The rarer the diamond is, the colorless the diamond is. The standard for grading color is to evaluate each stone against the main set by assigning a letter grade from “D” (colorless) to “Z” (light yellow).
Color is one of the 4Cs that impact the appearance and value of a diamond. When light hits the facet, some of the rays get scattered into a rainbow of colors, then reflect off the stone’s interior facets and bounce back to our eyes in flashes of color. This is known as the fire of a diamond.
If a diamond crystal has observable color in it, its ability to reflect light decreases in comparison to a colorless diamond. Hence, the fire and sparkle both get affected.
The normal color grading of diamonds refers to the lack of colors. The less the color, the higher the color grade will be. Fancy colored diamonds are available in various colors like pink, green, blue, and yellow and the color grading improves as the color becomes strong in the stones.
In case of the white diamonds, the color grade is measured on a scale ranging from D to Z.
Colorless Diamonds (D, E, F): D is the highest color grade. Stones of color grade are almost colorless and icy white. E and F color graded diamonds have very slight traces of color in them. This group of diamonds is the most expensive and rarest.
Nearly Colorless (G, H, I, J): This color grade displays nearly no color. This group of diamonds appear colorless to the naked eye. These diamonds are less expensive than the D-F group and are often used as the central stones in rings.Faint Color (K, L, M): Diamonds in this color grade possess a slight tint of yellow that can be seen even with the naked eye. Due to this, these diamonds are not as desirable as the two previous groups. They are also not as rare or as expensive as the other two groups mentioned above.
Very Light Color (N, O, P, Q, R): This group of diamonds has visible color, a tint of yellow or brown. There is very little demand for such diamonds and they are available at a much low price range. Most reputed jewellers avoid dealing in this category of diamonds for making ornaments.
Light Color (S-Z): The diamonds belonging to this color grade exhibit easily noticeable yellow or brown tint. As they are placed at the low end of the color grade, they are among the least expensive diamonds. Such diamonds are usually not considered for making ornaments.

